What is a perm - how does it come about?
What is a perm?
A perm is the chemical transformation process to make curls or waves in straight hair, or on the contrary, to smooth curly and wavy hair. The current method was invented around 1906.[1].
What happens to the hair?
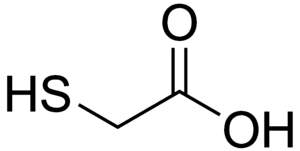
The thioglycolic acid Fig. 1
Externally, the hair itself consists of many very thin threads of keratin, which in itself, three long chains of amino acids, swirls in a triple helix. These are held within the chains by certain forces and bonds in their form. These compounds and the resulting forms are genetically determined. The two major compounds that hold these forms are hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds, where the hydrogen bonds are pure interactions but not chemical bonds. The so-called hair dryer wave is achieved only with water, a real perm over chemical methods. In the hair dryer wave, the water breaks the hydrogen bonds, thus loosening up the hair. The heat of the hair dryer now evaporates the water, and the hair takes on the styled shape. By an internal tension of the hair, they recede very quickly, by combing, blow-drying and washing, into their original form. In a perm, the hair proteins, so the keratin, "denatured". Denaturing means a protein that has solid forms to work, to deform. This is done by the influence of chemicals or by heat, so when cooking an egg, the proteins are denatured in the egg, which is why this hard. In the hair, the disulfide bridges of keratin, more specifically the amino acid cysteine as part of keratin, are split. This is done by thioglycolic acid and its salts. Hair loosening preparations usually include a pH stabilizer, e.g. Ammoniumhydrogencarbonat, which sets a pH of 7.5-9, ie an acidic pH, some emulsifiers and surfactants, and the thioglycolic acid. Subsequently, with an oxidizing agent, usually hydrogen peroxide, the disulfide bridges are restored, and thus brought back strength in the hair [2].
How does the perm process work?
First, with a preparation containing a pH stabilizer, some emulsifiers and surfactants, and cysteine (thioglycolic acid only rarely, as cysteine is gentler), the hair is loosened up. This process lasts between 10 and 30 minutes, but can be cured by heat, e.g. be accelerated by a heat hood. Subsequently, the hair is thoroughly washed to get rid of cysteine residues. After washing, the hair is brought into shape, and with an oxidizing agent, here usually hydrogen peroxide given strength again. In contrast to the hair dryer wave, a permanent wave lasts a much longer time, but will also return by an internal tension in the hair, and by frequent washing, blow drying and combing the original shape of the hair[3].
Are there any problems or consequences due to perms?
Yes there is. The thioglycolic acid namely decomposes at elevated temperatures to hydrogen sulphide (SH2) and sulfur oxides (S2O, SO2, SO3), which are highly toxic, also produces ammonia, which can lead as a gas in the long term to severe lungs and eye damage. If you do not fit here with the dryer hood, this can have serious consequences. In addition, the hydrogen peroxide attacks the hair pigment, and is therefore used for bleaching. The permanent wave itself does not cause hair damage (which is not wanted, such as destroying the melanin when bleaching) [4].
Source:
Wikipedia[1][4]
Article on the return of perm[3]
Articles on perm - types, duration, mode of action [2]




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!