Ceramides - The natural skin barrier
What are ceramides?
Ceramides are a subgroup of sphingolipids, and they make up our double lipid layer. It has different types, of which the ceramide I type accounts for most of the horny layer, the outermost layer of skin[1].
What are ceramides chemically?
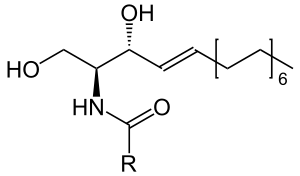
Fig. 1 The basic structure of ceramides, with sphingosine head, and a fatty acid residue (R)
Ceramides consist of four parts, sphingosine as a "head", a fatty acid as a "base", an amide as a linker and a residue in place of a hydroxide group on sphingosine. This residue can be a hydrogen - ceramide, a saccharide - glycosphingolipid, or a phosphocholine - sphingomyeline. Ceramide I is a fatty acid that binds linoleic acid as a fatty acid, so it has a lack of this fatty acid with a sub-production of ceramide I, and thus an imbalance in the horny layer, serious consequences for health and skin appearance. In addition, it strengthens the hair structure by better bonding the dandruff of the hair strands[2].
This double-lipid layer keeps foreign bodies from penetrating the body and also protects the skin from drying out. Ceramides are formed by first sphingosine with serine and an acyl-CoA, produced by the coenzyme A, it follows the amide esterification with a fatty acid to ceramide. The three best known types of ceramide can be determined by the inclusion angle (α) of the two chains. For example, α = 0 ° Type A, 0 ° <α <180 ° Type B and α = 180 ° Type C. The sphigosine base and the degree of hydroxylation of the Fatty acid decide the further name [3]. The ceramides also play a role in the mode of action of antidepressants [4].
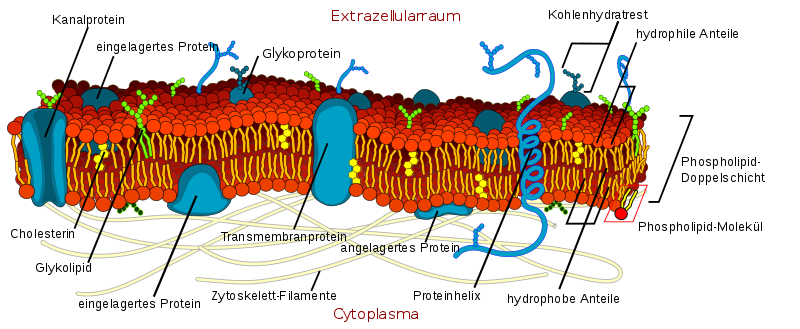
Fig. 2 Detailed illustration of the horny layer
Why are they in cosmetics?
If the body does not produce enough ceramide in the skin, it will cause it to dry out, as well as hypersensitivity (atopic dermatitis) or psoriasis. Ceramide I added to cosmetics can balance this balance of the skin and protect it from the effects of missing ceramide[5].
Sources:
Wikipedia[1][5]
Scientific article on ceramides in dermatology[2][3]
Scientific article on ceramides in neuroscience[4]
Image sources: Wikimedia Commons, Flickr. All image rights go to the owners of the images.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!